How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers
A scatter plot (also called a scatterplot, scatter graph, scatter chart, scattergram, or scatter diagram) is a type of plot or mathematical diagram using Cartesian coordinates to display values for typically two variables for a set of data. If the points are coded (color/shape/size), one additional variable can be displayed. The data are displayed as a collection of points, each having the. You just need to turn the position variable into a factor and then reverse its levels: require(dplyr) df% mutate(position = factor(position), position = factor(position, levels = rev(levels(position))) And then with your code you'd get. Python Data Types Python Numbers Python Casting Python. Getting Started Mean Median Mode Standard Deviation Percentile Data Distribution Normal Data Distribution Scatter Plot Linear Regression Polynomial Regression Multiple Regression Scale Train. The reverse method reverses the sorting order of the elements.
- How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers Free
- How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers List
- How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers Using
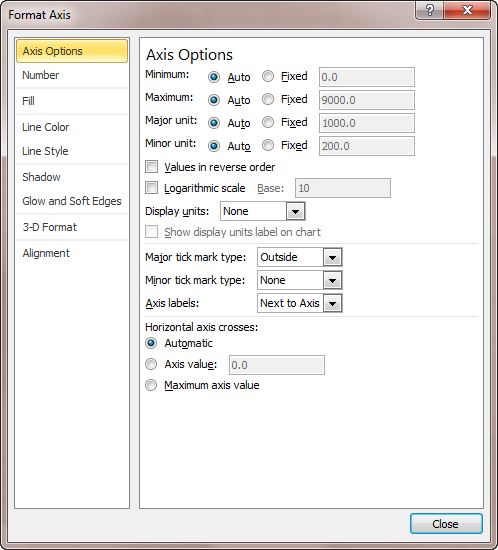
The scales of a graph determine the reference points for data displayed on the graph. A graph scale includes a vertical or horizontal axis line, tick marks for specific values or categories, and tick labels.

Types of scales
Graphs can have several types of scales, often on the same graph on different axes. A continuous scale is a sequential numeric scale with an infinite number of points between values. A categorical scale displays distinct, related groups of data; the categories are equally spaced and the space between the categories has no meaning.
How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers Free
Other types of scales include time scales, which display equally spaced time units (for example, day, month, quarter, year), and probability or percent scales, which are logarithmic and show the probability or percentage of observations that fall at or below certain values.
X-, Y-, and Z-scales
When you plot two variables in Minitab, you usually display the y variable on the vertical or y-axis to represent the response and the x variable on the horizontal or x-axis to represent the predictor. When you plot variables in three dimensions, the x and y variables usually represent the predictor variables and the z variable usually represents the response.
A scatter plot of y vs x with varying marker size and/or color.
How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers List
| Parameters: |
|
|---|---|
| Returns: |
|
| Other Parameters: |
|
See also
plot- To plot scatter plots when markers are identical in size and color.
Notes
How To Do Reverse Order For Scatter Plot In Mac Numbers Using
- The
plotfunction will be faster for scatterplots where markersdon't vary in size or color. - Any or all of x, y, s, and c may be masked arrays, in whichcase all masks will be combined and only unmasked points will beplotted.
- Fundamentally, scatter works with 1-D arrays; x, y, s, and cmay be input as 2-D arrays, but within scatter they will beflattened. The exception is c, which will be flattened only if itssize matches the size of x and y.
Note
In addition to the above described arguments, this function can take adata keyword argument. If such a data argument is given, thefollowing arguments are replaced by data[<arg>]:
- All arguments with the following names: 'c', 'color', 'edgecolors', 'facecolor', 'facecolors', 'linewidths', 's', 'x', 'y'.
Objects passed as data must support item access (data[<arg>]) andmembership test (<arg>indata).
